The content of the article
In Russia, bats are found in the North Caucasus region. One of the varieties of bats is the large horseshoe.
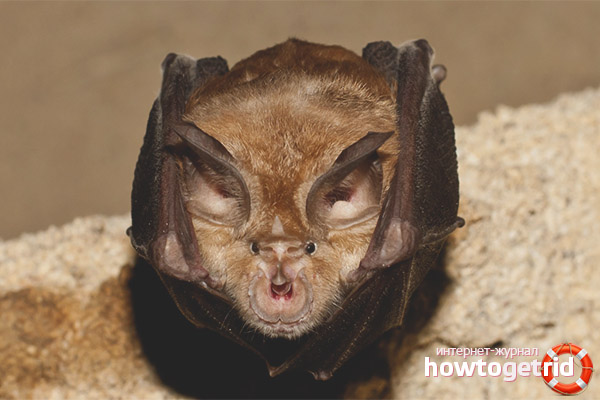
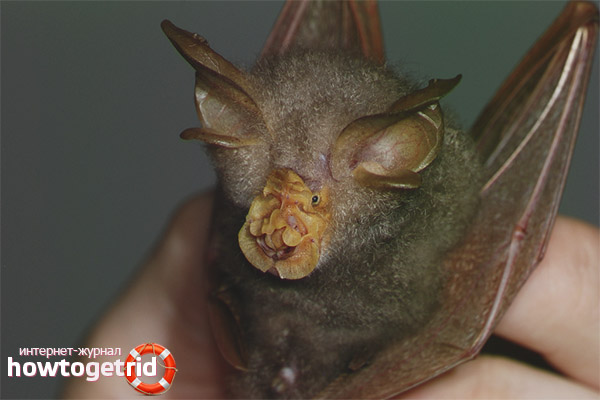
Appearance
The length of the horseshoe is 10 cm, of which 3 cm is the tail, 7 cm is directly the length of the body. Such a bat weighs a little, on average 27 grams, but the wingspan for such a small mammal is quite impressive, reaching 40 cm.
The nose of the horseshoe has a rather interesting shape, on it are skin growths resembling a horseshoe. Thanks to this shape of the nose, the large horseshoe got its name. The growths help create sounds.
Bat species similar to the great horseshoe
Bats like a horseshoe can be found all over the world. There are 80 varieties in total, but only five species inhabit European countries. The large horseshoe breech and its varieties have a distinctive characteristic feature: during sleep, these bats use their wings as a blanket, and wrap themselves in them.
Lifestyle and Nutrition
Horseshoe horses prefer to get food for themselves at night. Insects, mainly bugs, act as food for them. Having outlined once a night hunting route, horseshoes subsequently rarely change it. The animals catch insects with their teeth or use their webbed wings for this. Wings for horseshoes are a kind of hands, they send bugs directly to their mouth. Such bats eat small insects right on the fly, and with large insects it’s a bit more complicated, they eat them, hanging on a tree branch. Thanks to skin growths on the nose, horseshoes can make sounds even while eating.
Mating a large horseshoe
Horseshoes breed not every year. Females reach puberty with only two years, and sometimes by three years. In connection with this circumstance, subject to the disappearance of places suitable for the residence of a horseshoe carrier, its number may sharply decrease.
Usually large horseshoes mate in late autumn, before hibernating. The development of the embryo directly depends on the ambient temperature, the warmer the faster the maturation of the embryo. In this regard, pregnant females are combined in one colony. Only one individual is born. At first, the horseshoe carrier cubs are completely blind and naked, but they grow so fast that when they reach 22 days, they begin to fly. When the young come 30-40 days, they can catch their own food and fly long distances.
People responsibility
The population of bats, or rather large horseshoes, has declined by 90% over the previous century, and continues to decline at the present time. Who is to blame for this? Of course, man. It is the people to blame for the disappearance of a large number of horseshoe-carrier habitats. The development of rural land at the beginning of the last century led to a decrease in the pristine appearance of fields and meadows. Poisonous substances used in agriculture destroy insects, and, as a result, bats that feed on them. All this led to the inclusion of large horseshoes in the list of endangered species of animals.
Features of the behavior of a large horseshoe
They rarely leave their cubs alone, as they, left unattended, create a lot of noise and scream, which can give shelter to a colony of bats.
When the horseshoe hibernates, it produces 10 breaths in one minute, just before leaving the winter hibernation their number per minute increases and reaches 200 breaths.
When the horseshoe flies, it catches ultrasonic waves, moving its ears for this 60 times in one second.










Submit